Next-Generation Sequencing Data from a CUT&RUN Study of R. toruloides IFO0880 Cse4 and Orc1 Binding Sites
Themes: Conversion
Keywords: Genome Engineering, Genomics
Citation
Schultz, C.J., Cao, M., Mejia, A., Zhao, H. June 10, 2021. “IFO0880 Cse4 and Orc1 CUT&RUN.” NCBI BioProject.
Overview
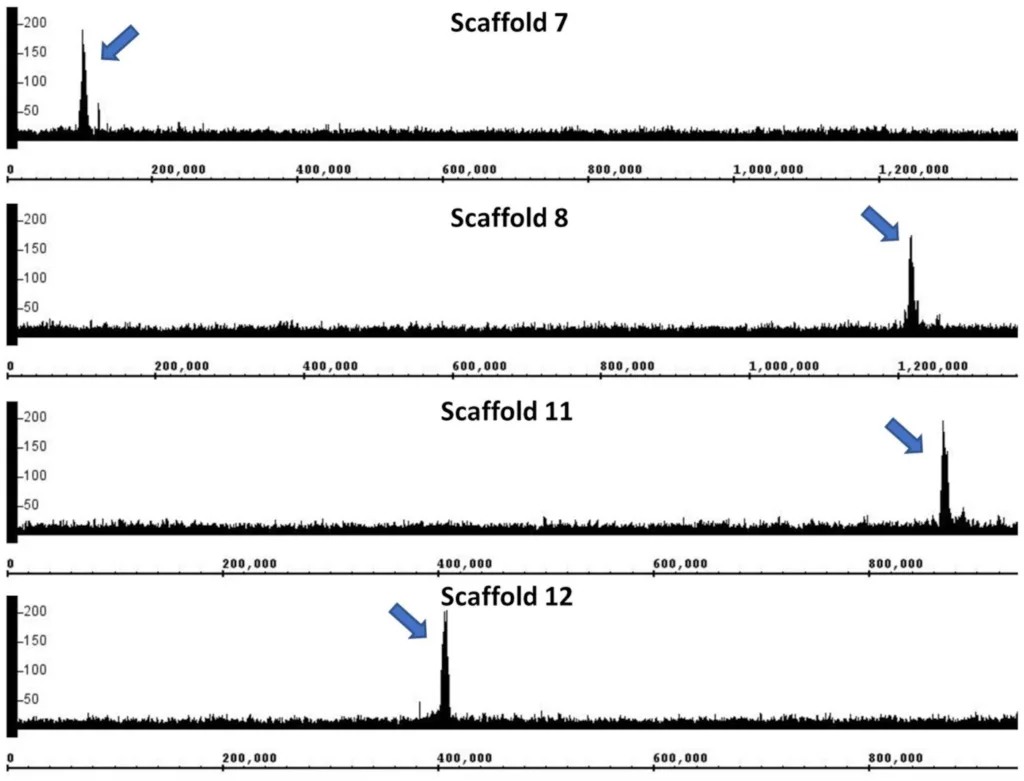
Rhodotorula toruloides has been increasingly explored as a host for bioproduction of lipids, fatty acid derivatives and terpenoids. Various genetic tools have been developed, but neither a centromere nor an autonomously replicating sequence (ARS), both necessary elements for stable episomal plasmid maintenance, has yet been reported. In this study, cleavage under targets and release using nuclease (CUT&RUN), a method used for genome-wide mapping of DNA–protein interactions, was used to identify R. toruloides IFO0880 genomic regions associated with the centromeric histone H3 protein Cse4, a marker of centromeric DNA. Fifteen putative centromeres ranging from 8 to 19 kb in length were identified and analyzed, and four were tested for, but did not show, ARS activity. These centromeric sequences contained below average GC content, corresponded to transcriptional cold spots, were primarily nonrepetitive and shared some vestigial transposon-related sequences but otherwise did not show significant sequence conservation. Future efforts to identify an ARS in this yeast can utilize these centromeric DNA sequences to improve the stability of episomal plasmids derived from putative ARS elements.
Data
Sequence Read Archive Sequencing Data
Download (4.2 KB) includes:
- DNA Sequences
- Primers
- tBLASTn hits