In silico Evaluation of Plant Nitrification Suppression Effects on Agroecosystem Nitrogen Loss
Themes: Sustainability
Keywords: Biomass Analytics, Field Data, Modeling
Citation
Hartman, M.D., Burnham, M., Parton, W.J., Finzi, A., DeLucia, E.H., Yang W. Dec. 4, 2022. “In silico Evaluation of Plant Nitrification Suppression Effects on Agroecosystem Nitrogen Loss.” FigShare. DOI: 10.6084/m9.figshare.20113463.v1.
Overview
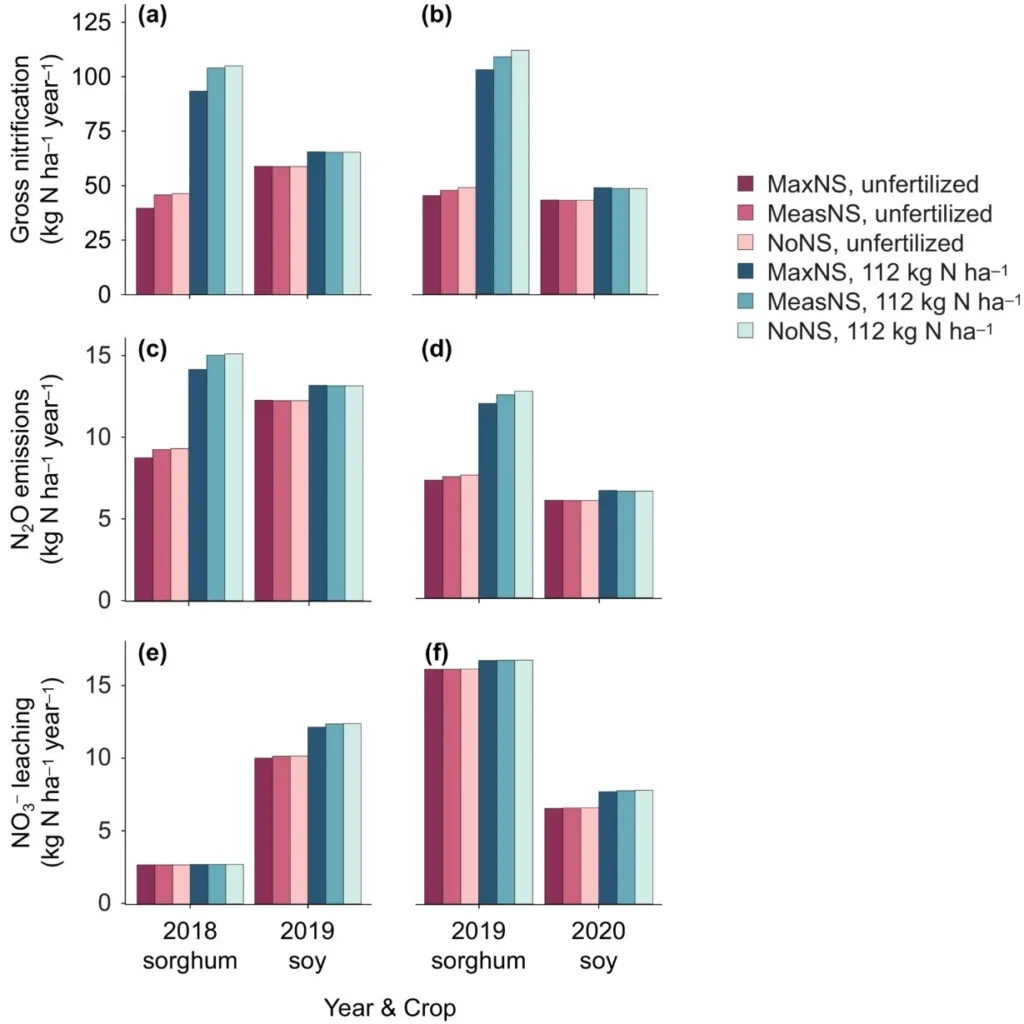
This dataset includes the source code for the updates to DayCent (Daily Century model). DayCent is a biogeochemical model that simulates fluxes of carbon and nitrogen among the atmosphere, vegetation, and soil to produce daily fluxes of nitrogen gases, CO2 flux from heterotrophic soil respiration, soil organic carbon and nitrogen, net primary production, and H2O and NO3-leaching. The major update to the model is adding a “GrassTree” crop type to better represent large bioenergy crops and grasses within the model. Data, including biomass and soil data, trial yields, plot history, and weather data, are available to reproduce the simulations shown in “In silico Evaluation of Plant Nitrification Suppression Effects on Agroecosystem Nitrogen Loss.”