Economic Perspective of Ethanol and Biodiesel Coproduction from Industrial Hemp
Themes: Conversion, Feedstock Production
Keywords: Economics, Modeling
Citation
Viswanathan, M.B., Cheng, M.H., Clemente, T.E., Dweikat, I., Singh, V. May 25, 2021. Data from: “Economic Perspective on Ethanol and Biodiesel Coproduction from Industrial Hemp.” University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign. DOI: 10.13012/B2IDB-1141487_V1.
Overview
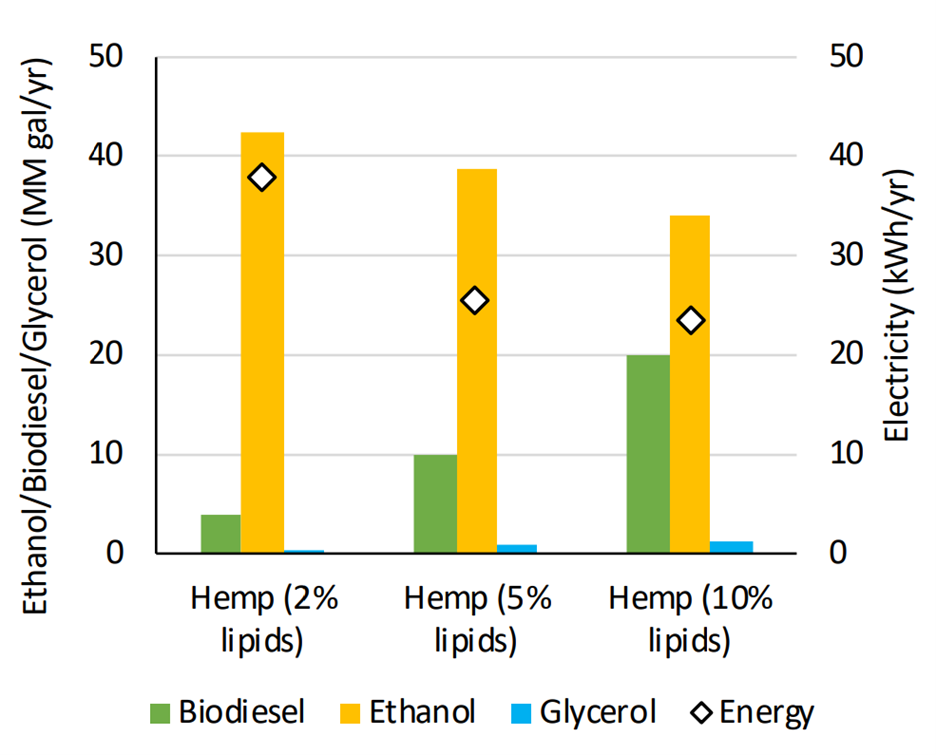
In this study, the economics of producing biofuels from an industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa) genotype – 19m96136 was investigated. A lignocellulosic biofuel plant, hourly consuming 85 metric tons of hemp biomass was modeled in SuperPro Designer®. The integrated bioenergy plant produced hemp biodiesel and bioethanol from lipids and carbohydrates, respectively. The structural composition of the industrial hemp plant was analyzed in a previous study. The data obtained was used to simulate feedstock composition in SuperPro Designer®.
The simulation results indicated that Hemp containing 2% lipids can yield up to 3.95 million gallons of biodiesel annually. On improving biomass lipid content to 5 and 10%, biodiesel production increased to 9.88 and 19.91 million gallons, respectively. The breakeven unit production cost of hemp biodiesel with 2, 5, and 10% lipid containing hemp was $18.49, $7.87, and $4.13/gallon, respectively. The biodiesel unit production cost when utilizing 10% lipid-containing hemp was comparable to soybean biodiesel at $4.13/gallon. Furthermore, sensitivity analysis revealed the possibility of a 7.80% reduction in unit production cost upon a 10% reduction in hemp feedstock cost. Furthermore, industrial hemp was capable of producing between 307.80 and 325.82 gallons of total biofuels per hectare of agricultural land than soybean.
Data
Illinois Data Bank includes:
- Operating parameters for plant properties and product costs
- Capital operating cost breakdown