Discovery, Characterization, and Application of Chromosomal Integration Sites in the Hyperthermophilic Archaeon Sulfolobus islandicus
Themes: Conversion
Keywords: AI/ML, Gene Editing, Genome Engineering, Metabolic Engineering
Citation
Boob, A.G., Zhang, C., Pan, Y., Zaidi, A., Whitaker, R.J., Zhao, H. Dec. 1, 2025. Integration-Sites-M.16.4. GitHub.
Overview
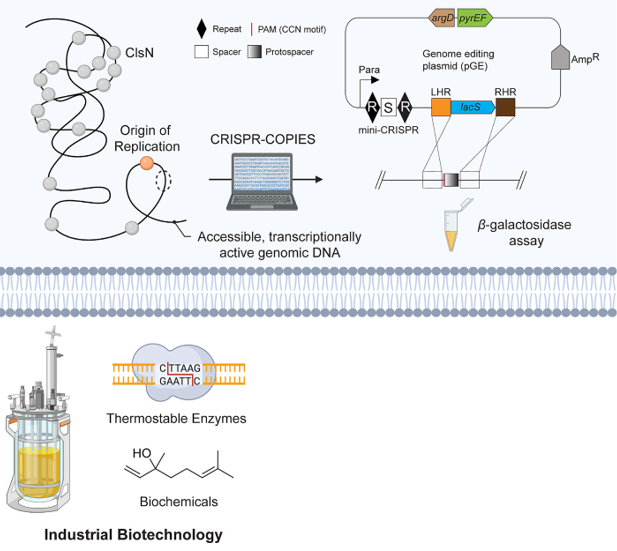
Sulfolobus islandicus, an emerging archaeal model organism, offers unique advantages for metabolic engineering and synthetic biology applications owing to its ability to thrive in extreme environments. Although several genetic tools have been established for this organism, the lack of well-characterized chromosomal integration sites has limited its potential as a cellular factory. Here, we systematically identified and characterized 13 artificial CRISPR RNAs targeting eight integration sites in S. islandicus using the CRISPR-COPIES pipeline and a multi-omics-informed computational workflow. We leveraged the endogenous CRISPR-Cas system to integrate the reporter gene lacS and validated heterologous expression through a β-galactosidase assay, revealing significant positional effects. As a proof of concept, we utilized these sites to genetically manipulate lipid ether composition by overexpressing glycerol dibiphytanyl glycerol tetraether (GDGT) ring synthase B (GrsB). This study expands the genetic toolbox for S. islandicus and advances its potential as a robust platform for archaeal synthetic biology and industrial biotechnology.
Data
GitHub: Python scripts
- CRISPR-COPIES parameters
- Integration sites
- Oligos, primers, genes, plasmids, strains